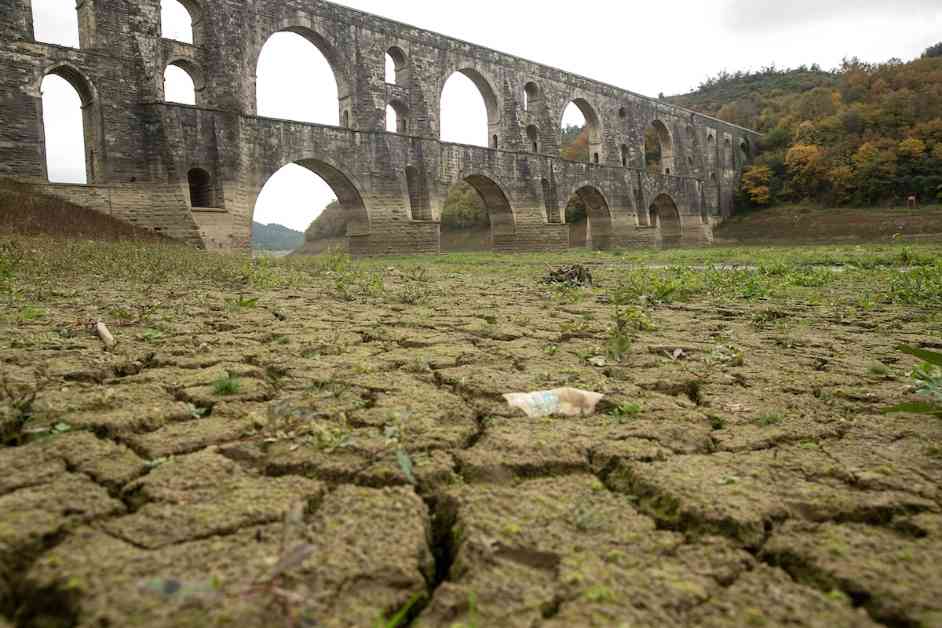
The impact of climate change on water supply has become a pressing issue worldwide, with recent studies highlighting the urgency of stronger water management strategies. Lorenzo Rosa, a principal investigator at Carnegie Science, and Matteo Sangiorgio, a researcher at the Polytechnic University of Milan, conducted a comprehensive analysis to quantify water scarcity under different global warming scenarios. This research sheds light on the challenges humanity faces in balancing water supply and demand in a changing climate.
Understanding the Water Gap Dilemma
According to the study by Rosa and Sangiorgio, more than 4 billion people live in regions that experience water scarcity for at least one month each year. This water scarcity, known as a “water gap,” occurs when the demand for water surpasses the natural availability, leading to depleted water sources like rivers, lakes, and aquifers. As climate change disrupts precipitation patterns and alters the water cycle, the stress on water resources intensifies, further exacerbating the existing challenges faced by communities worldwide.
The researchers quantified water gaps under different warming scenarios, revealing that the current annual water gap is nearly 458 billion cubic meters. This gap is projected to increase by 6% under a 1.5 degrees Celsius warming scenario and by 15% under a 3 degrees Celsius warming scenario. These findings underscore the critical need for proactive measures to address water scarcity and ensure sustainable water management practices in the face of climate change.
Implications for Water Resource Management
To bridge the growing water gap, water resource managers and policymakers must consider various strategies to enhance water supply and reduce demand. Investing in resilient infrastructure for water storage, exploring water reuse and desalination technologies, and promoting efficient irrigation practices are key steps to mitigate water scarcity. Farmers can also play a significant role by adopting water-efficient crop cultivation methods and irrigation technologies to optimize water use in agriculture.
The study emphasizes that while water scarcity affects entire regions, vulnerable and impoverished populations bear the most severe consequences. Economic and institutional factors play a crucial role in determining the extent of water scarcity and its impact on society and the environment. As global warming intensifies, the delicate balance between water supply and demand is likely to deteriorate, posing a significant threat to economic development, societal well-being, and aquatic ecosystems.
In conclusion, the study “Global water gaps under future warming levels” published in Nature Communications underscores the urgent need for coordinated efforts to address water scarcity in the face of climate change. By implementing sustainable water management practices, investing in innovative technologies, and fostering collaboration at local, regional, and global levels, we can work towards a more resilient and water-secure future for all.
Cristen, a writer of fiction and nonfiction, holds a JD and an Ocean & Coastal Law Certificate from the University of Oregon School of Law. She is the author of the short story collection “The Smallest of Entryways” and the travel biography “Ernest’s Way: An International Journey Through Hemingway’s Life”. Subscribe to our newsletter for exclusive updates on environmental issues and solutions.