Global Warming Weakens Earth’s Strongest Ocean Current
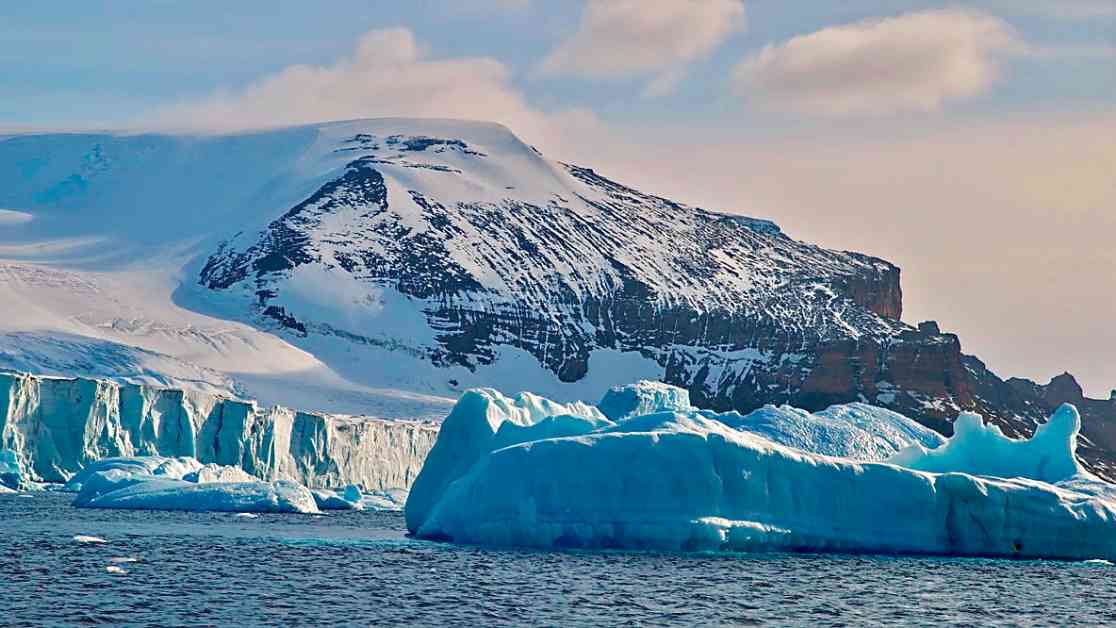
An international team of scientists recently published a study in the journal Environmental Research Letters, projecting that the world’s most powerful ocean current, the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC), will weaken by 20 percent within the next 25 years. This weakening is attributed to the influx of fresh water from melting Antarctic ice, a phenomenon that is directly linked to human-induced global warming. These findings have sparked concerns among experts, as a weakened ACC could lead to more climate variability, extreme weather events, and accelerated global warming.
A Vital Climate Engine Under Threat
Lead author Bishakhdatta Gayen, an associate professor of fluid mechanics at the University of Melbourne, emphasized the critical role of the ACC as one of Earth’s strongest climate engines. This vast ocean current, which flows unimpeded around the entire planet, carries an astonishing amount of water—more than 100 times the volume of all the world’s rivers combined. As it circles Antarctica from west to east, the ACC plays a crucial role in mixing water from the Pacific, Indian, and Atlantic ocean basins.
The Impact of a Weakened ACC
The repercussions of a weakened ACC are far-reaching and potentially catastrophic. Gayen warned that a slowdown in this current could lead to disruptions in the redistribution of heat, carbon dioxide, and other essential elements across the world’s oceans. This disruption could trigger the onset of marine heatwaves, toxic algal blooms, and other detrimental impacts on marine ecosystems. Additionally, a weaker ACC could contribute to accelerated sea level rise, exacerbating the threats posed by climate change.
The Southern Hemisphere at Risk
In recent years, the Southern Hemisphere has experienced unprecedented ocean warming, particularly off the coast of eastern Australia. This temperature increase, combined with record-breaking ocean heatwaves in the Tasman Sea and the South Pacific, has had devastating effects on marine life and coral reefs in the region. The implications of a weakened ACC extend beyond the Southern Ocean, with potential ripple effects on ocean currents and climate patterns in the Northern Hemisphere.
Navigating Uncertainties and Challenges
While the study’s projections offer valuable insights into the future of the ACC, there remain significant uncertainties regarding the rate and extent of ice melting in Antarctica. Gayen stressed the importance of monitoring and understanding these changes to accurately predict the impact on the world’s oceans. Co-author Taimoor Sohail highlighted the complex interplay between temperature and salinity changes in the Southern Ocean, underscoring the need for further research to elucidate these dynamics.
Preserving Earth’s Natural Balance
The implications of a weakened ACC extend beyond climate and ocean dynamics, impacting the delicate balance of ecosystems around Antarctica. Gayen emphasized the role of the ACC as a physical barrier that shields Antarctica’s unique ecosystems from external influences. Should the current weaken, the influx of invasive species and disruptions to marine ecosystems could have far-reaching consequences for the region’s biodiversity.
Supporting Independent Climate Journalism
The research and reporting on crucial environmental issues, such as the impact of global warming on ocean currents, rely on the dedication and support of organizations like Inside Climate News. As a nonprofit organization committed to providing free access to vital climate news, Inside Climate News relies on reader donations to sustain its work. Your contribution can help fund in-depth reporting on the pressing environmental challenges facing our planet and ensure that this critical information reaches a wider audience.
In conclusion, the study’s findings underscore the urgent need for global action to address climate change and its repercussions on ocean currents and ecosystems. By supporting independent climate journalism and staying informed about the latest scientific research, individuals can contribute to a more sustainable future for our planet. Together, we can work towards preserving Earth’s natural balance and mitigating the impacts of global warming on our oceans and environment.