California’s Renewable Energy Success: A Myth Debunked
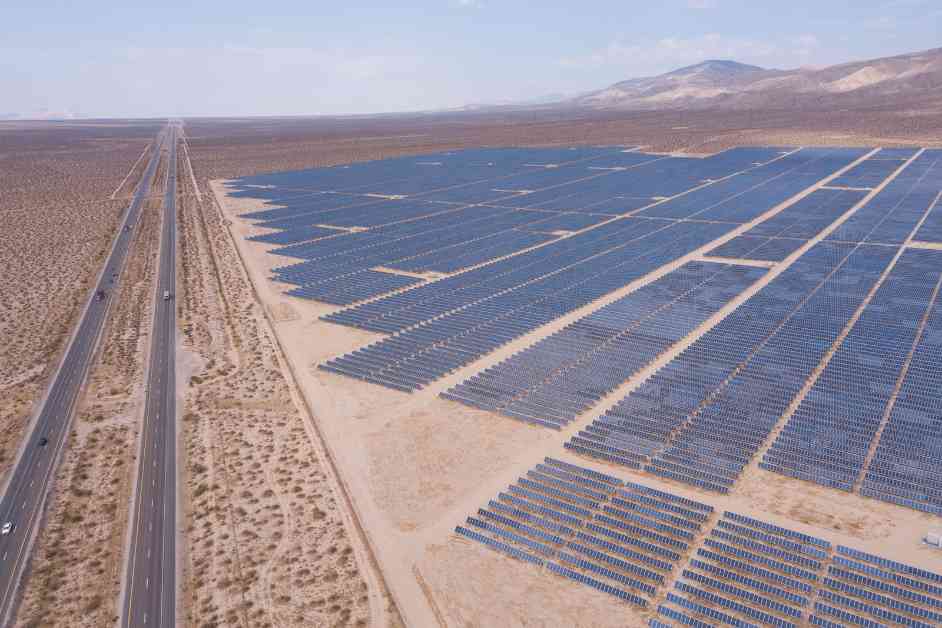
California is leading the charge in renewable energy, showcasing its reliability and potential for a sustainable future. A recent study published in Renewable Energy sheds light on the state’s remarkable progress in harnessing renewable power sources to meet electricity demands. The study, led by Mark Z. Jacobson of Stanford University, reveals a groundbreaking achievement: renewables supplied 100 percent of California’s electricity demand for up to 10 hours on 98 out of 116 days last year. This milestone not only demonstrates the reliability of renewable energy but also highlights the state’s capacity to exceed its grid’s needs by up to 162 percent, allowing for surplus energy exports or storage in batteries.
Challenges Amidst Progress
Despite the success of renewable energy in California, challenges persist. The state grapples with high electricity rates, not due to renewables but because of utility-related issues. Recent devastating wildfires, like the Camp Fire, sparked by power lines, have led utilities to pass on costs to consumers. Wildfires, exacerbated by climate change, pose a threat to electrical infrastructure, necessitating the burying of transmission lines. Investigations into the causes of wildfires underscore the vulnerability of power lines, especially during extreme weather conditions.
Rapid Transition to Clean Energy
California’s energy landscape is rapidly transitioning towards clean energy sources, with renewables accounting for about half of the state’s power generation. Solar output surged by 31 percent, and wind by 8 percent between 2023 and 2024. The state also doubled its battery capacity, equivalent to the output of four nuclear power plants, reducing fossil fuel consumption significantly. These technological advancements have enhanced grid flexibility, allowing for efficient management of electricity demand, particularly during peak hours.
Consumer Adoption of Solar and Batteries
The adoption of solar panels and batteries by consumers has played a crucial role in reducing grid demand. The installation of batteries with solar panels enables consumers to store excess energy for nighttime usage, thereby alleviating strain on the grid. The rise in battery adoption, from 13 percent in 2023 to 38 percent in 2024, signifies a growing trend towards self-sufficiency and energy independence among Californians.
Economic Implications of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy integration has economic implications, impacting electricity prices for consumers. States with higher renewable energy penetration, like South Dakota, Montana, and Iowa, have lower electricity prices due to increased reliance on wind and hydropower. In contrast, California, despite its 47 percent renewable power contribution, faces higher electricity costs, attributed to the aftermath of wildfires and associated expenses borne by ratepayers. The economics of renewable energy underscore the complex interplay between technological advancements and economic feasibility.
Looking Towards a Sustainable Future
California’s success in renewable energy and battery technology signifies a paradigm shift towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future. Despite challenges posed by climate change and utility-related issues, the state’s commitment to clean energy underscores the viability and reliability of renewables. As California continues to lead the way in renewable energy innovation, the myth of renewables’ unreliability is debunked, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable energy landscape.