Scientists Discover Fertilizer’s Impact on Pollinators
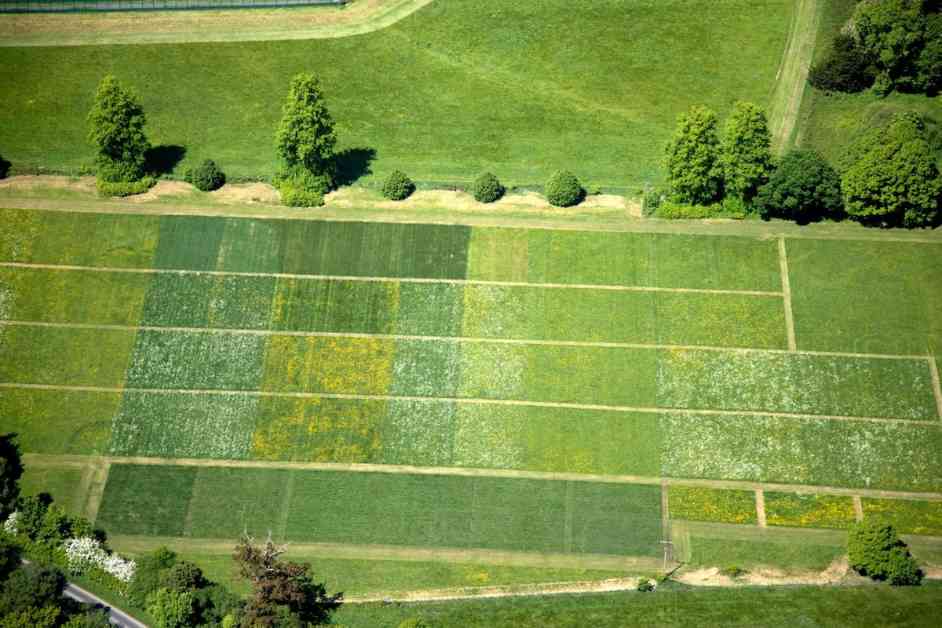
A groundbreaking study conducted at the Park Grass Experiment in Hertfordshire, England, has revealed alarming consequences of high fertilizer use on pollinators and flowering plants. Led by researchers at the University of Sussex and Rothamsted Research, this study sheds light on how fertilizers negatively impact these crucial organisms and the delicate ecosystem they support.
Effects of High Fertilizer Use on Pollinators and Flowers
Over a two-year period, researchers examined the effects of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium fertilizers on the abundance of pollinators and flowering plants at the iconic Park Grass Experiment site. The results were staggering, showing a 50% decline in pollinators and a five-fold decrease in flowering plants in areas with high fertilizer use compared to untreated plots.
Untreated land plots boasted 95% more pollinators, with bees showing a remarkable 9.35 times higher abundance in these areas. In contrast, plots with high fertilizer levels saw an increase in flies and beetles, further highlighting the detrimental impact of excessive fertilization on biodiversity.
Sustainable Solutions for Maintaining Biodiversity
The study’s lead researcher, Nicholas Balfour, emphasized the urgent need to address the link between fertilizer use and declining pollinator populations. By implementing land management strategies like using lime or clover, researchers found that plots with lime had significantly higher pollinator abundance, species richness, flower abundance, and flower species richness compared to plots without lime.
The findings underscore the importance of reducing fertilizer use on agricultural grasslands to preserve biodiversity, enhance soil health, and mitigate carbon emissions. The study authors advocate for well-designed policies that promote sustainable nutrient management practices, such as incorporating nitrogen-fixing legumes and minimizing nitrogen inputs while balancing phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium levels.
Implications for Environmental Conservation and Sustainable Agriculture
As the global agricultural sector grapples with the challenge of balancing productivity with environmental stewardship, the study’s findings offer valuable insights into the critical role of fertilizers in shaping ecosystems. By adopting practices that prioritize biodiversity conservation and soil sustainability, farmers and policymakers can work towards a more resilient and ecologically sound agricultural landscape.
In conclusion, the study serves as a clarion call for sustainable land management practices that prioritize biodiversity conservation while ensuring food security and environmental integrity. By rethinking our approach to fertilization and embracing nature-based solutions, we can pave the way for a more sustainable and harmonious coexistence with the natural world.
Now, imagine walking through a lush field teeming with vibrant flowers and buzzing with the gentle hum of bees. The sight and sound of nature’s intricate dance fill your senses with awe and wonder, reminding you of the delicate balance that sustains life on our planet. As you witness the beauty and biodiversity of this ecosystem, consider the profound impact of human actions on pollinators and flowering plants. Take a moment to reflect on the interconnectedness of all living beings and the responsibility we bear to protect and preserve the rich tapestry of life that surrounds us. Let this moment of contemplation inspire you to take small steps towards a more sustainable future, where harmony between humans and nature is not just a dream but a reality we create together.