Potential Health Risks of Microplastics in Medical Infusion Bags
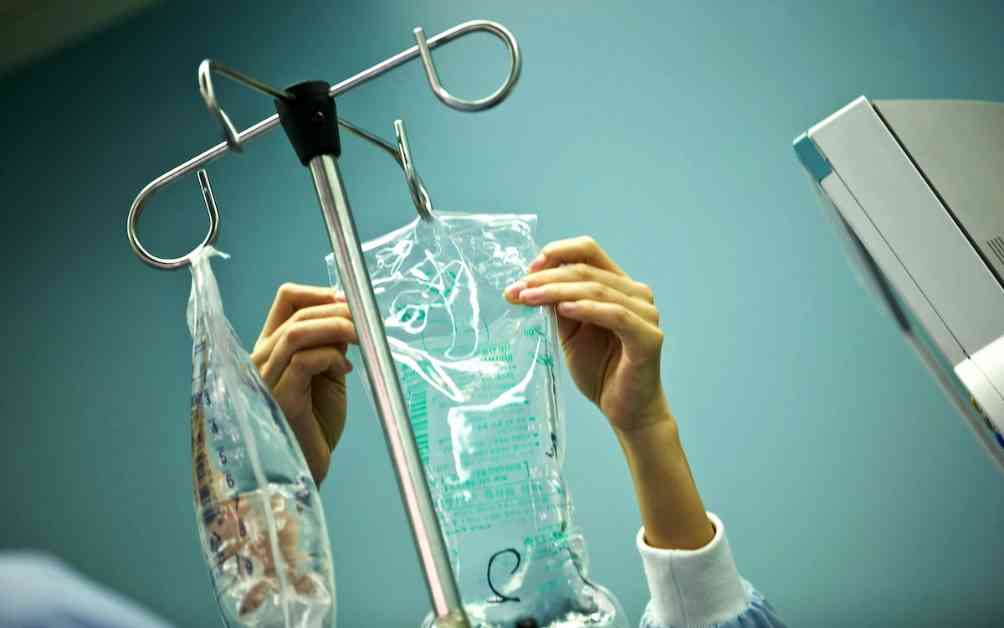
Microplastics, tiny plastic particles that are invading our environment, have now found a potential pathway into the human body through medical infusion bags. A recent study published in Environment & Health has revealed that a single medical infusion bag, typically used for intravenous treatments, could release a significant number of microplastic particles into a person’s bloodstream. These findings raise concerns about the health risks associated with microplastics entering our bodies through medical procedures.
Investigating Microplastic Contamination in Medical Infusion Bags
Medical infusion bags, commonly made from materials such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and others, are essential for administering intravenous fluids, nutrients, and medications. Researchers conducted a study to determine whether these bags could be a source of microplastic contamination. By testing commercial infusion bags containing IV saline solutions, researchers discovered that these bags could release a significant number of microplastic particles into a person’s bloodstream during an infusion.
The study involved collecting liquid samples from two different brands of commercial infusion bags made from PP and filtering them to analyze the plastic particles present. The results showed that a single bag could release up to 7,500 microplastic particles into the bloodstream during an infusion. For patients who require larger volumes of fluids, such as those undergoing abdominal surgery or suffering from dehydration, the number of microplastics entering the body could be substantially higher.
The implications of these findings are particularly concerning in the context of rising global temperatures and an increased risk of heat-related illnesses. Patients receiving IV fluids for conditions like heat illness or dehydration could potentially be exposed to tens of thousands of microplastic particles, posing a potential risk to their health.
Implications for Health and Safety
The study authors highlighted the need for further research to investigate the presence of microplastics in a wider range of infusion bags, considering factors such as material quality, storage conditions, and manufacturing processes. They also emphasized the importance of implementing measures to reduce microplastic contamination in medical settings.
One of the key recommendations from the study was to store medical infusion bags in conditions that minimize microplastic breakdown, such as limiting exposure to heat and UV light. Additionally, the authors suggested the use of highly efficient filtration systems during intravenous infusions to reduce the risk of microplastic exposure. They also proposed the development of innovative infusion system designs using materials resistant to microplastic shedding to enhance safety standards in medical practices.
In conclusion, the study underscores the importance of addressing the potential health risks associated with microplastic contamination in medical infusion bags. By implementing strategies to minimize microplastic exposure and conducting further research on this topic, healthcare providers can ensure the safety and well-being of their patients.
As the world grapples with the challenges of environmental pollution and its impact on human health, it is crucial to remain vigilant about the sources of microplastic contamination and take proactive steps to mitigate these risks. By raising awareness about the potential health hazards of microplastics in medical settings, we can work towards creating a safer and healthier environment for all.
Subscribe today to stay informed about the latest developments in environmental health and sustainability. Together, we can make a positive impact on our planet and protect the well-being of future generations.